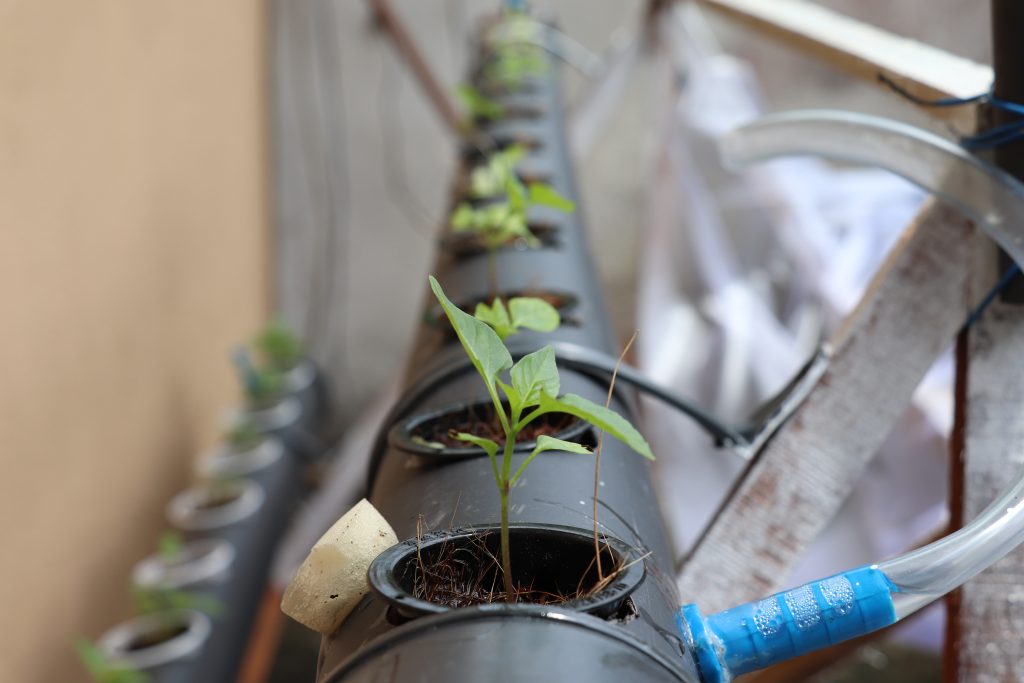

All about Hydroponics growing method
What is Hydroponics?
The word hydroponics comes from the Greek for “working with water” and is a method of growing plants in a nutrient-rich liquid rather than in the soil. In this article, we are talking about the basics of hydroponics.
This can be started outdoors in warm weather or indoors all year round and has many benefits, including:
- No weeding
- Fast growth
- High yields in a small space
- No insects flying
- Clean vegetable crops
- Ease of harvesting
- Constant quality without insects or soil-related diseases
One of the best things about hydroponics is that it can be done in a small space: a balcony or terrace, a small patio, the roof of an apartment building and even indoors. Since this is a stand-alone system, a hydroponic configuration can be scale to any size you want (given the weight of the water) to suit yourself, a friend or family.
Methods of Hydroponics
Active and Passive hydroponic systems
There are many different types of hydroponic systems, but most are considered active or passive. An active system uses pumps to circulate water, while a passive system uses gravity to move the liquid or uses absorbent material to attract water to the roots.
Whether active or passive, most household hydroponic crops are closed systems that recirculate the nutrient solution through the system over and over again, saving water. In an open system, water is neither captured nor reused.
Media-based systems
Although you can only grow plants in water, for large and heavy plants like tomatoes, it does help to provide some form of support for plant roots as a growing medium.
There are many types of inert growing media that can be used to hold the roots in place. Common substrates used in media-based system include;
- Sand
- Gravel
- Polyethene fibre
- Peas
- Coconut fibre
- Perlite
- Vermiculite
- Clay Granules
- Glass beads
- Rock wool
To keep the culture media moist, one of the following configurations are generally used. There are 3 basic types of hydroponic systems for the media-based hydroponics systems. Let’s go through about each method.
1. Wick System
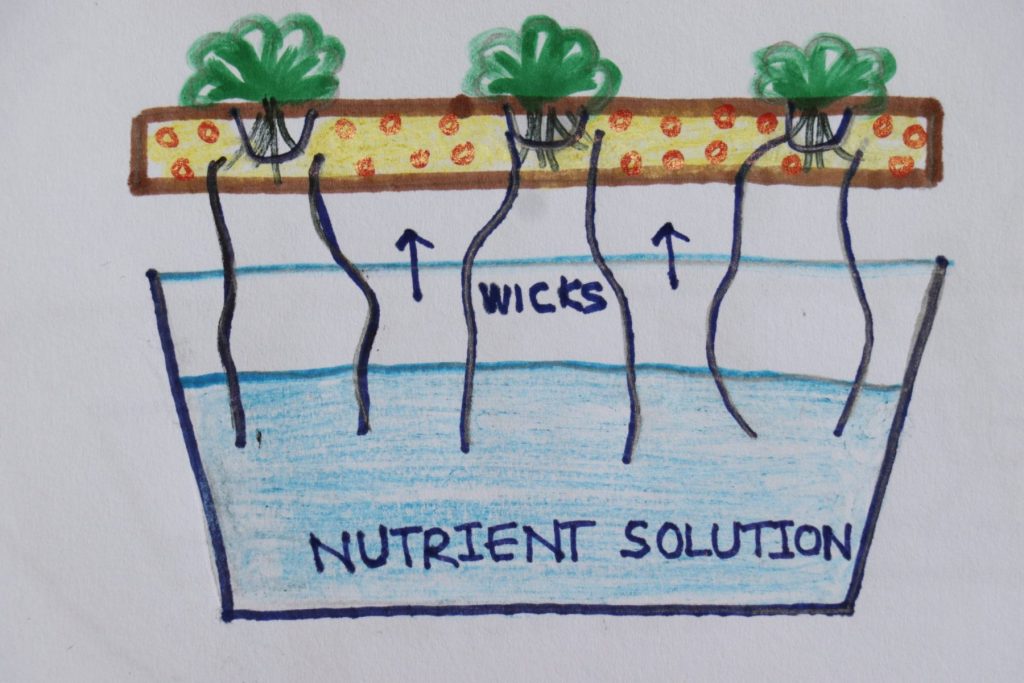
Wick system is one of the most basic media-based methods, works as an automatic watering tank. Pieces of cotton or nylon rope guide the aerated nutrient solution, by capillary action, from a reservoir located under the plants to the upper growth medium, passively providing moisture to the plants.
Plants suitable to grow – It works best for plants that don’t need a lot of water, such as herbs like rosemary, thyme, and oregano, as well as fast-growing micro-greens and deep-rooted plants like beets or radish.
Drawbacks are the wick method does not always provide enough water to completely saturate the media. So, even though wick systems are simple to use, they are best reserved for small plants or if you have limited space.
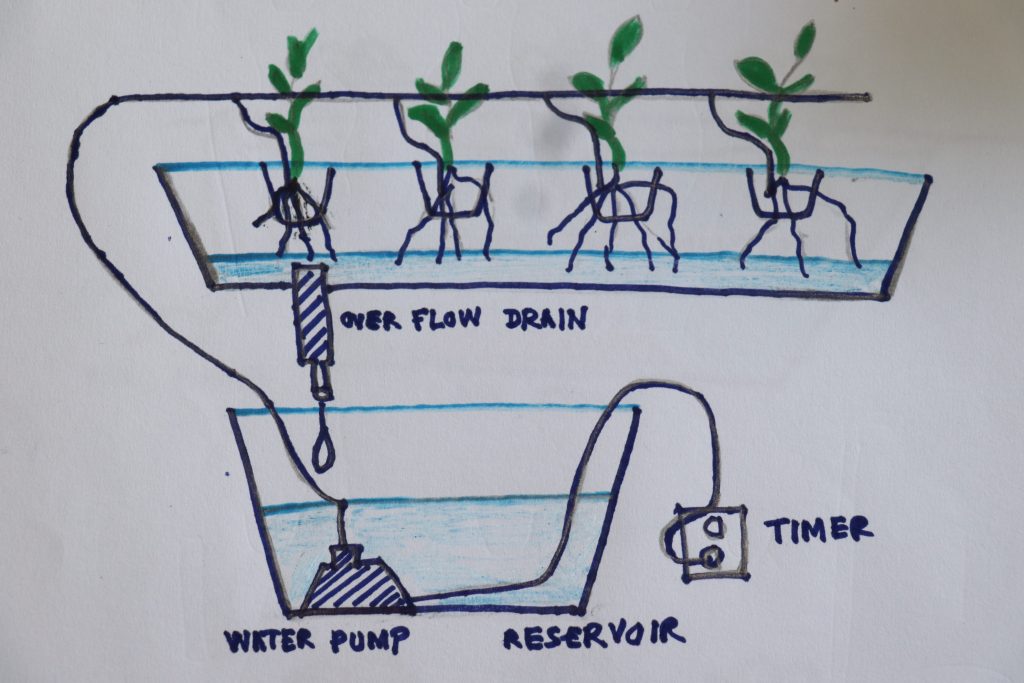
2. Ebb and Flow System
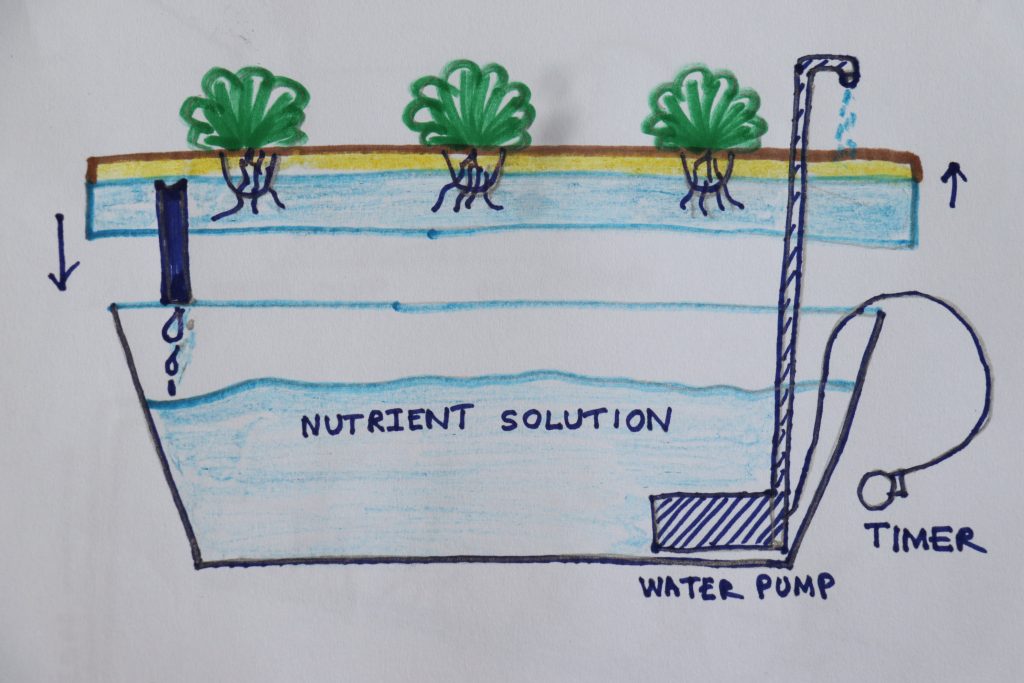
Using a tray and a reservoir system you can start this easily. An ebb and flow or flood and drainage system can be active or passive, depending on the amount of work you want to do. Plants growing in this method should be potted in a neutral medium and only sit an inch or two beneath the surface of the water. This allows the root system to absorb as much as it needs while receiving proper aeration.
Provide water to the roots at regular intervals, usually several times a day, and then let it drain. You can do this manually by trapping water at one end of the system in a bucket after it has passed through the medium and pouring it at the other end of the system a few hours later.
This type of system can be easily automated using tubes and a submersible pump connected to a timer to move the water, making it an active system.
3. Drip System
The drip systems are also active. They provide a constant flow of water to each plant via a drip line. The excess water eventually seeps into a tank under the planter and is recirculated through a drip line again by a pump.
In this case, the root system is not exposed. The plants are grown in your standard hydroponic medium like coco coir or vermiculite. The water literally drips from the hoses onto the medium and is controlled by a timer to go on and off at specific intervals.
Liquid-based systems
Liquid-based systems do not use any type of growing medium to support plant roots. Instead, the plants are hung in mesh pots or other holding structures with their roots exposed to a nutrient solution that has been aerated with an aquarium-type air pump.
4. Nutrient film technique (NFT)
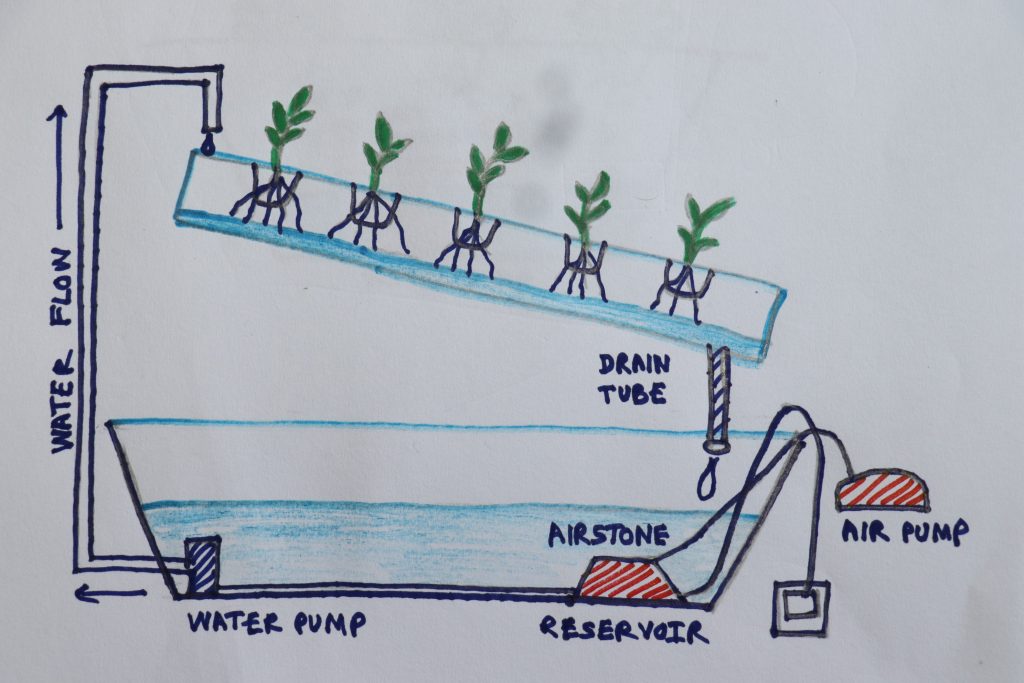
The Nutrient film technique (NFT) continuously provides a thin layer of aerated nutrients to plants via a system of sloping horizontal channels. This also involves the use of a reservoir and pump system.
Plants are placed in holes along the top of the channels and nutrients are pumped to the top side of each channel and flow by gravity to the bottom end where they are pumped through the circuit. The channel must be positioned at an angle so that the water flows over the lower tips of the roots and back into the reservoir.
5. Deep water culture
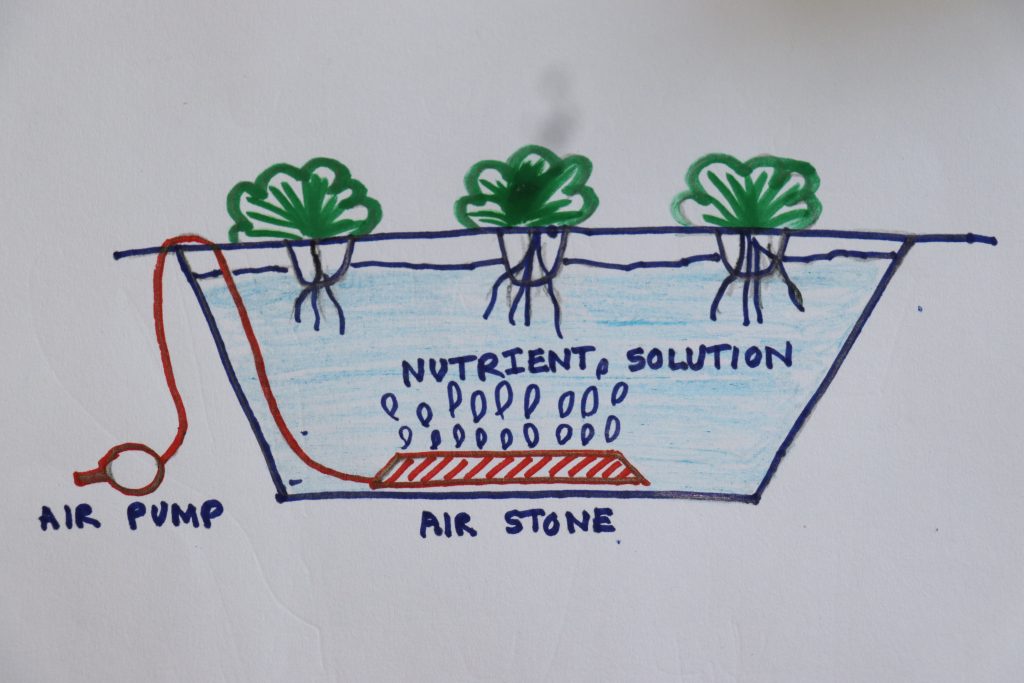
plants hang with their roots in a nutrient solution. For a raft-type method, the polystyrene sheets float on the surface of the water. Holes cut in the Styrofoam hold the mesh pots and prevent them from sinking into the water. Plants grow with their roots submerged in an aerated nutrient solution under the raft.
Injecting air through a pump and various hoses allows the grower to control the size of the bubbles and the amount of aeration. The aerated with oxygen bubbles that flow upward from the bottom of the reservoir. This provides all the oxygen for the root system needs.
Plants suitable to grow – It is a great method of growing lettuce, herbs, and other light crops that do not grow enough to sink the raft.
6. Aeroponics method
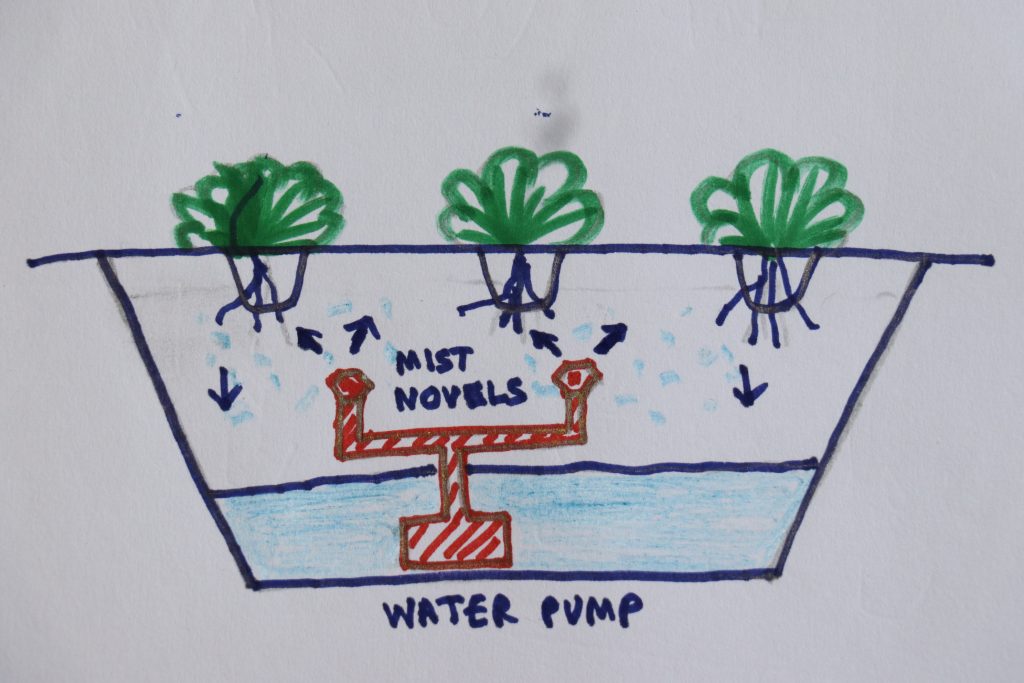
Aeroponics is a system in which the roots are maintained continuously or discontinuously in an environment saturated with fine drops (mist or spray) of nutrient solution.
The method requires no substrate and involves the growth of plants with their roots suspended in a deep air or a growth chamber with the roots periodically moistened with a fine mist of atomized nutrients. Excellent ventilation is the main advantage of aeroponics.
Water quality and fertilizers
Since water is the most important element in hydroponics, have him test yours before you begin. Chemicals in city water can be harmful to your plants, and high concentrations of mineral salts can affect the balance of fertilizers.
Although you can mix yours, there are organic and chemical fertilizers specially designed for hydroponic growing systems. Some are specially designed for leafy crops, while others are formulated to grow flowers and fruits. The use of garden fertilizers intended for use in the soil will not give the desired growth of the plant and can clog pipes and fittings.
A slightly acidic solution (5.5-6.5) is optimal for plants to make the best use of available nutrients, so test the pH of the solution regularly.
To prevent nutrients from becoming too concentrated, add water to keep the solution level stable and change the solution regularly to keep it fresh. Keep in mind that different plants have different needs and you may need to adjust your nutrient solution accordingly.
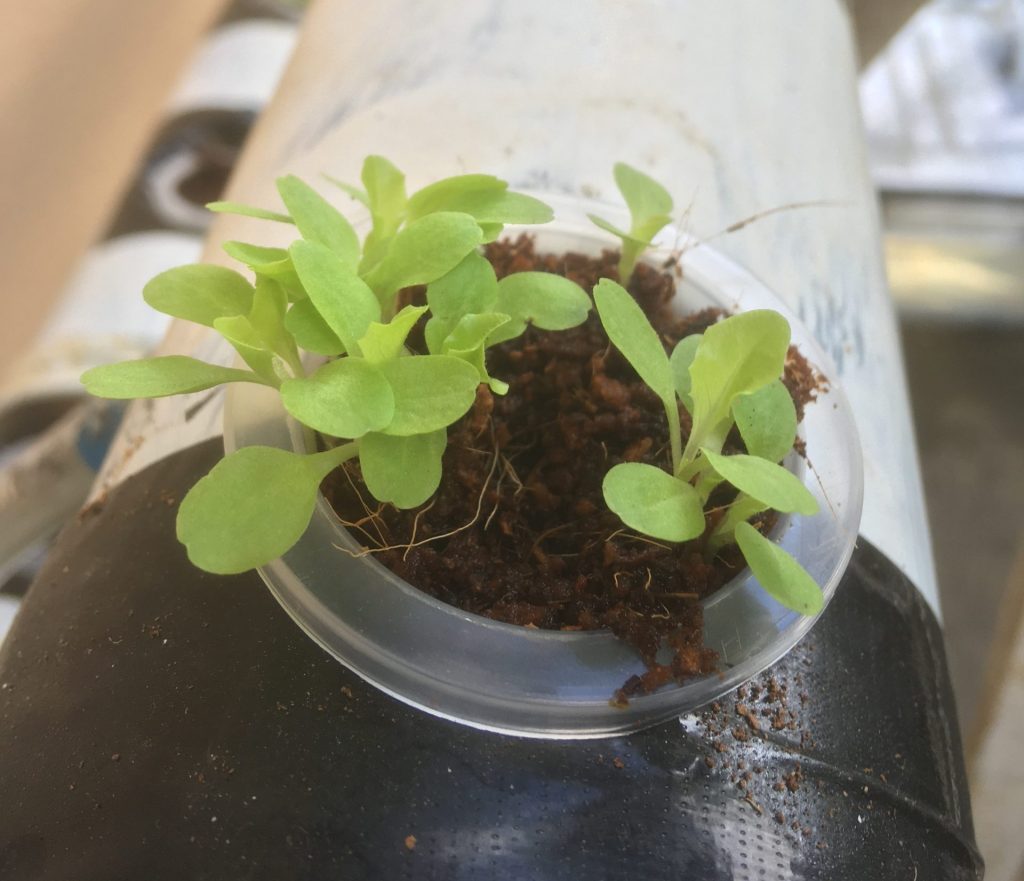

Plants for hydroponic systems If you buy plants to use in your system, wash the soil from the roots to ensure you do not introduce soil-borne diseases. One of the joys of hydroponic gardening is that by removing the soil, you don’t have to worry about many disease problems. Good sanitation practices will help keep your system trouble-free.
The rapid growth rates of many crops such as lettuce, Swiss chard, arugula, and other green vegetables prevent pests from establishing themselves.
If you grow your plants from seeds, you can start them in peat granules, Rockwool cubes, or in stopper trays filled with a soilless mix. Transfer them to your hydroponic system when the roots have grown to the bottom of the cork.
Pollination becomes a problem when growing fruit plants indoors. In an outdoor garden, tomatoes are pollinated by the wind. To simulate this indoors, turn on a fan or press and shake the vines when they are in bloom. Look for self-pollinated cucumber varieties that carry all the female flowers.
Last Touch
Commercial growers turn to hydroponics like never before. The ideals surrounding these growth techniques touch on topics that interest most people, such as helping to end world hunger and making the world a cleaner place. People from all over the world have built or bought their systems to grow fresh and tasty food for family and friends. Ambitious people strive to make their dreams come true by earning a living in their backyard greenhouse by selling their produce at local markets and restaurants. In the classroom, educators realize the incredible applications that hydroponics can have to teach children science and gardening.
The speed of hydroponic research increases at exponential rates as many benefits are realized. Associated disciplines, such as Aeroponics and Aquaponics, are leading the way, and no one knows what the future holds for such exciting green technology. General Hydroponics will continue to drive innovation and provide cutting-edge technology and resources.
4 thoughts on “All about Hydroponics growing method”
Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Thank you Mr LarrySwall for your feedback. Yes, we are trying to make this guidance in a more practical way. Sure we will add those in future articles.
By
Hey! Would you mind if I share your blog with my myspace group? There’s a lot of folks that I think would really enjoy your content. Please let me know. Thank you
Yes, you can share. Thanks